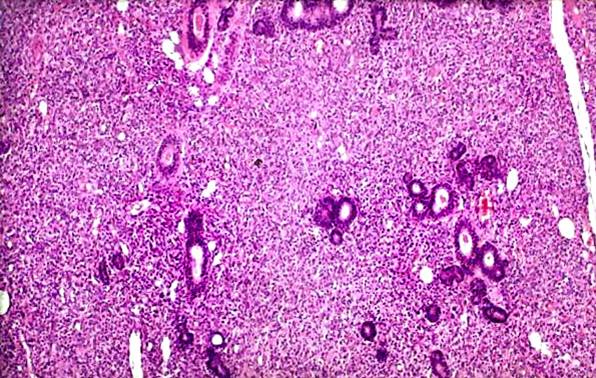
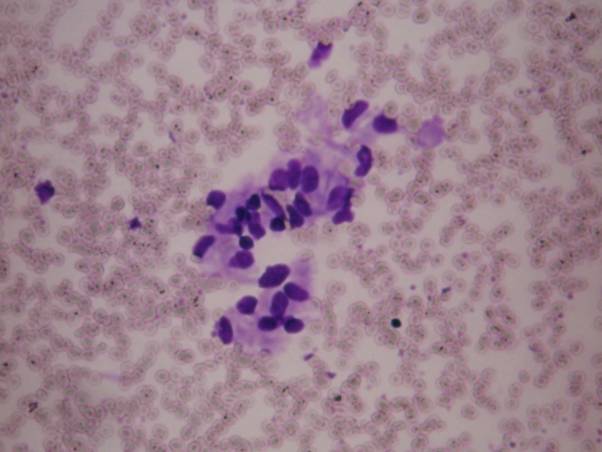
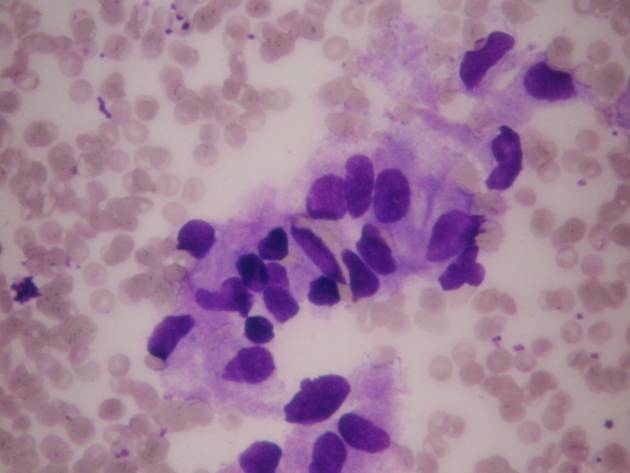
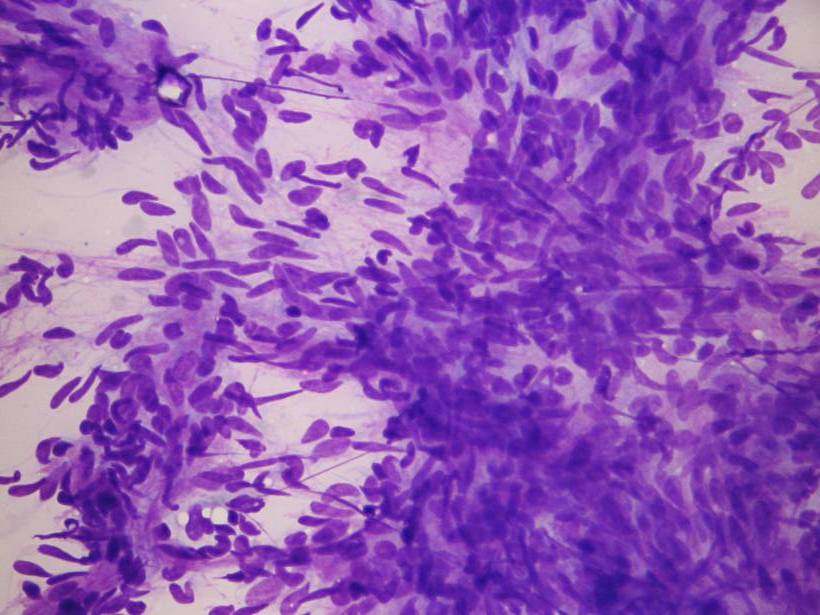
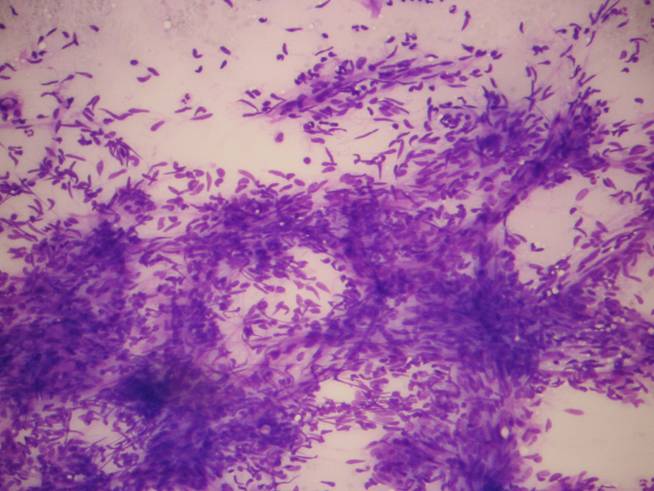
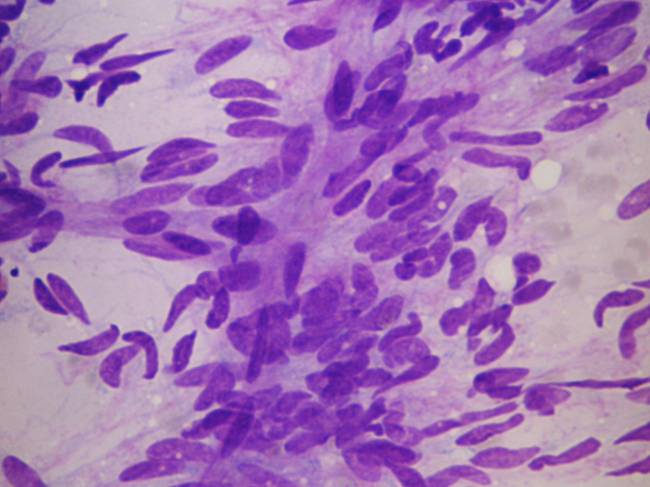
Haemangioma of the infants
It is usually a congenital, large and painless lesion. The aspirate contains a large amount of blood in which proliferative endothelial cells are seen. Since it is usually only followed up without surgery, the correct diagnosis in this early age is very important.
Haemangioma of the infants - cytology Lymphangioma
There is only yellowish slightly bloody fluid in the aspirate which hardly contains any cellular material. The cystic lesion refills usually in a couple of minutes after the aspiration.
Peripheral nerve sheet tumor
The tumor is connected to the facial nerve in the parotid region, which results in the fact that the aspiration procedure is painless. The cytologic pattern resembles the histologic one, even Verocay body like structures are found. The cells are arranged in sheets; they are elongated, benign-looking mesenchymal cells.